Keul-o-test®
E. coli
KGST310
A rapid, one step test for the qualitative detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli) antigens in human faeces.
For professional in vitro diagnostic use only.
Intended Use
The E. coli Device test is a rapid chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of E. coli O157 antigens in human faeces specimens to aid in the diagnosis of E. coli infections.
Synthesis
E. coli O157:H7 is one of hundreds of strains of the bacterium Escherichia coli. Although most strains are harmless, this strain produces a powerful toxin that can cause severe illness. E. coli O157:H7 has been found in the intestines of healthy cattle, deer, goats, and sheep.
E. coli O157:H7 was first recognized as a cause of illness in 1982 during an outbreak of severe bloody diarrhea; the outbreak was traced to contaminated hamburgers. Since then, more infections in all over the world have been caused by eating undercooked ground beef than by any other food.
Principle
The E. coli Device is a qualitative lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of Escherichia coli antigen in human faeces samples. The membrane is pre-coated with monoclonal antibodies against E. coli O157 antigens on the test line region. During testing, the sample reacts with the particle coated with anti-E. coli O157 antibodies which was pre-dried on the test strip. The mixture moves upward on the membrane by capillary action. In the case of a positive result the specific antibodies present on the membrane will react with the mixture conjugate and generate a coloured line. A green coloured band always appears in the control line and serves as verification that sufficient volume was added, that proper flow was obtained and as an internal control for the reagents.
Precautions
- For professional in vitro diagnostic use only.
- Do not use after expiration date.
- The test should remain in the sealed pouch until use.
- Do not use the test if pouch is damaged.
- Follow Good Laboratory Practices, wear protective clothing, use disposal gloves, do not eat, drink or smoke in the area.
- All the specimens should be considered potentially hazardous and handled in the same manner as an infectious agent.
- The test should be discarded in a proper biohazard container after testing.
- The test must be carried out within 2 hours of opening the sealed bag.
Storage and stability
Store as packaged in the sealed pouch either at refrigerated or room temperature (2-30ºC/36-86ºF). The test is stable through the expiration date printed on the sealed pouch. The test must remain in the sealed pouch until use. Do not freeze.
Materials provided
- Devices
- Instructions for use
- Specimen collection vial with buffer
Materials required but not provided
- Specimen collection container
- Disposable gloves
- Timer
Specimen collection and preparation
Collect sufficient quantity of faeces (1-2 g or mL for liquid sample). Stool samples should be collected in clean and dry containers (no preservatives or transport media). The samples can be stored in the refrigerator (2-4ºC/36-40ºF) for 1-2 days prior to testing. For longer storage the specimen must be kept frozen at -20ºC/-4ºF. In this case, the sample will be totally thawed, and brought to room temperature before testing.
For the enrichment culture test, stool sample is inoculated into a TSB medium and incubated overnight on a shaker at 37ºC. The test procedure use the enrichment culture as a stool sample.
Procedures
To process the collected stool samples (see illustration 1):
Use a separate specimen collection vial for each sample. Unscrew the cap of the vial and introduce the stick two times into the faecal specimen to pick up quite a lot of sample (200-300 mg) . Close the vial with the buffer and stool sample. Shake the vial in order to assure good sample dispersion. For liquid stool samples, aspirate the faecal specimen with a dropper and add 200-300 uL into the specimen collection vial with buffer.
Test Procedure (see illustration 2)
Allow the tests, stool samples and buffer to reach to room temperature (15-30ºC/59-86ºF) prior to testing. Do not open pouches until ready to perform the assay.
-
Remove the E. coli Device from its sealed pouch and use it as soon as possible.
-
Shake the specimen collection vial to assure a good sample dispersion. Break off the cap of the vial.
-
Use a separate device for each sample. Dispense exactly 4 drops or 100 uL into the specimen well (S). Start the timer.
-
Read the result at 10 minutes after dispensing the sample.
Illustration 1
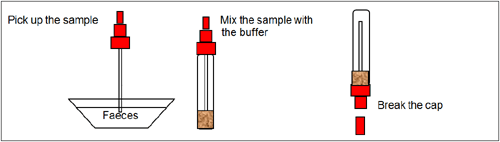
Illustration 2

Interpretation of results
Illustration 3
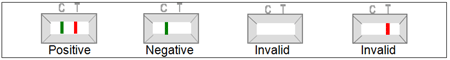
POSITIVE: Two lines appears across the central window in the result line region (red test line marked with the letter T) and in the control line region (green control line marked with the letter C).
NEGATIVE: Only one green band appears across the control line region marked with the letter C (control line).
INVALID: A total absence of the green control coloured band regardless the appearance or not of the red test line. Note: Insufficient specimen volume, incorrect procedural techniques or deterioration of the reagents are the most likely reasons for control line failure. Review the procedure and repeat the test with a new test. If the problem persists, discontinue using the test kit and contact you local distributor.
Notes on the interpretation of results
The intensity of the red coloured band in the result line region (T) will vary depending on the concentration of antigens in the specimen. However, neither the quantitative value, nor the rate of increase in antigens can be determined by this qualitative test.
Quality control
Internal procedural controls are included in the test:
- A green line appearing in the control line region (C). It confirms sufficient specimen volume and correct procedural technique.
Limitations
- E. coli Device will only indicate the presence of Escherichia coli in the specimen (qualitative detection) and should be used for the detection of E. coli O157 antigens in faeces specimens only. Neither the quantitative value nor the rate of increase in E. coli antigens concentration can be determined by this test.
- An excess of sample could cause wrong results (brown bands appear). Dilute the sample with the buffer and repeat the test.
- Some stool samples can decrease the intensity of the control line.
- If the test result is negative and clinical symptoms persist, additional testing using other clinical methods is recommended. A negative result does not at any time preclude the possibility of E. coli infection.
- This test provides a presumptive diagnosis of E. coli. All results must be interpreted together with other clinical information and laboratory findings available to the physician.
Expected values
Escherichia coli O157:H7 is a leading cause of foodborne illness. Based on a 1999 estimate, 73,000 cases of infection and 61 deaths occur in the United States each year.
Performance characteristics
Sensitivity
The detection of E. coli O157:H7 showed a 100% of concordance in sensitivity.
Specificity
The detection of E. coli O157:H7 showed a 85% of concordance in specificity.
PPV showed a 70% and NPV showed a 100%.
Exactitude
The detection of E. coli O157:H7 showed a 94% of concordance in exactitude.
Cross-Reactivity
It was performed an evaluation to determine the cross reactivity of E. coli Device. There is not cross reactivity with common gastrointestinal pathogens, other organisms and substances occasionally present in feces.
- Rotavirus
- Adenovirus
- Campylobacter
- Giardia lamblia
References
- Rangel, J. M., Sparling, P. H., Crowe, C., Griffin, P. M. & Swerdlow, D. L. 2005 Epidemiology of Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreaks, United States, 1982-2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 11, 603-609.
- Griffin, P.M. „The Epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7, other enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and the associated haemolytic uremic syndrome“. Epidemiol. Rev , 1991, 13:60-98.
Qualitätssicherung und Vorkommnisse
Sollten Sie den Eindruck eines Qualitätsmangels haben oder unklare oder ihrerseits falsch-positive oder falsch-negative Ergebnisse erhalten, bitten wir Sie, die betreffende Patientenprobe zurückzustellen und für einen Abruf für uns bereitzuhalten.
Bitte informieren Sie uns umgehend. Sie helfen uns dadurch die Sicherheit der Produkte und damit die Qualität zu gewährleisten.
 |
Hersteller: |

Günter Keul GmbH
Von-Langen-Weg 10
D-48565 Steinfurt
Tel.: 02551/2097 Fax.: 02551/80883
Web: www.keul.de
|
|