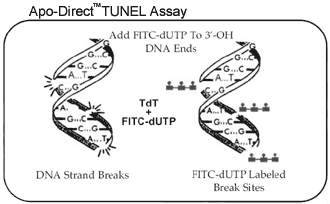
APO-DIRECT uses a directly conjugated two color TUNEL (Terminal deoxynucleotide transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling) assay to simultaneously label DNA strand breaks and total cellular DNA, to allow detection of apoptotic cells. Detection is achieved by flow or image cytometry or by fluorescence microscopy. Fluorescein-dUTP is the fluorescent label used in this kit to directly label DNA strand breaks.
The kit has several key characteristics:
- Single-step method to label DNA strand breaks in apoptotic cells;
- Unequivocal results (method is based on the gold standard TUNEL assay);
- Contains all reagents and controls.
The kit contains the instructions and all reagents required for the identification of apoptotic cells and also includes positive and negative control cells for assessing reagent performance. The reagents comprise washing, reaction and rinsing buffers for processing individual steps in the assay, along with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase enzyme (TdT), fluorescein deoxyuridine triphosphate (F-dUTP) (labels DNA strand breaks) and a propidium iodide and RNase A solution (counter stains total cellular DNA).
Although this methodology has been proven effective, its utility has previously been limited when a complete analysis is required for the cells and/or tissues under investigation. This limitation resulted from the techniques that were required to make the incorporated BrdU accessible for labeling. Since the duplex strands of DNA must be separated to make the BrdU epitope accessible for labeling, the conventional techniques for doing this, acid or heat denaturation, caused the simultaneous denaturation or loss of many cellular proteins. This made it difficult to perform other measurements of cell function or phenotype when these harsh methods were used. Phoenix Flow Systems, Inc. has introduced the patented SBIP (Strand Breaks Induced by Photolysis) methodology for its cell proliferation kits. This method does not require DNA denaturation to make the BrdU accessible and is therefore applicable in studies where preservation of antigens or other features of the cells is desired. The SBIP methodology first involves growing cells in the presence of BrdU. The BrdU incorporation sites are then sensitized to subsequent photolysis. The UV light induced breaks at these sites are then additionally labeled with bromolated
deoxyuridine triphosphate (BrdUTP) through a reaction catalyzed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). The BrdUTP sites are then identified using a fluorochrome labeled anti-BrdU antibody.
|